

* min range (inclusive) and the specified upper bound (exclusive).
MATH.RANDOM JAVA INCLUSIVE HOW TO
Though most of the cases can be easily fulfilled using ThreadLocalRandom, however, if you are more interested in how to generate random numbers in Java 8, here are few options to accomplish it using Java 8 import Math.random() also requires about twice the processing and is subject to synchronization.We can create 2 different Random objects by passing same seed. It’s better to use the original one than routing through it. Math.random() uses Random.nextDouble() internally.If you are only interested in getting the int as the random number, you should choose the Random.nextInt(n) as this option is more efficient and less biased.Here are some of the advantages of using Random.nextInt over Math.random() Generate random number with in given rangeĭouble random = (int)(Math.random() * ((max - min) + 1)) You do this by adding the min value (last part of expression +min) Shift this range up to the range that you are targeting.To get a specific range of values, We should multiple by the magnitude of the range of values we want covered ( * ( Max - Min )).Math.random() generates a double value in the range [0,1).If the bound is Math.random() * ((max - min) + 1)) +min.We don’t need explicit initialize with the ThreadLocalRandom class.
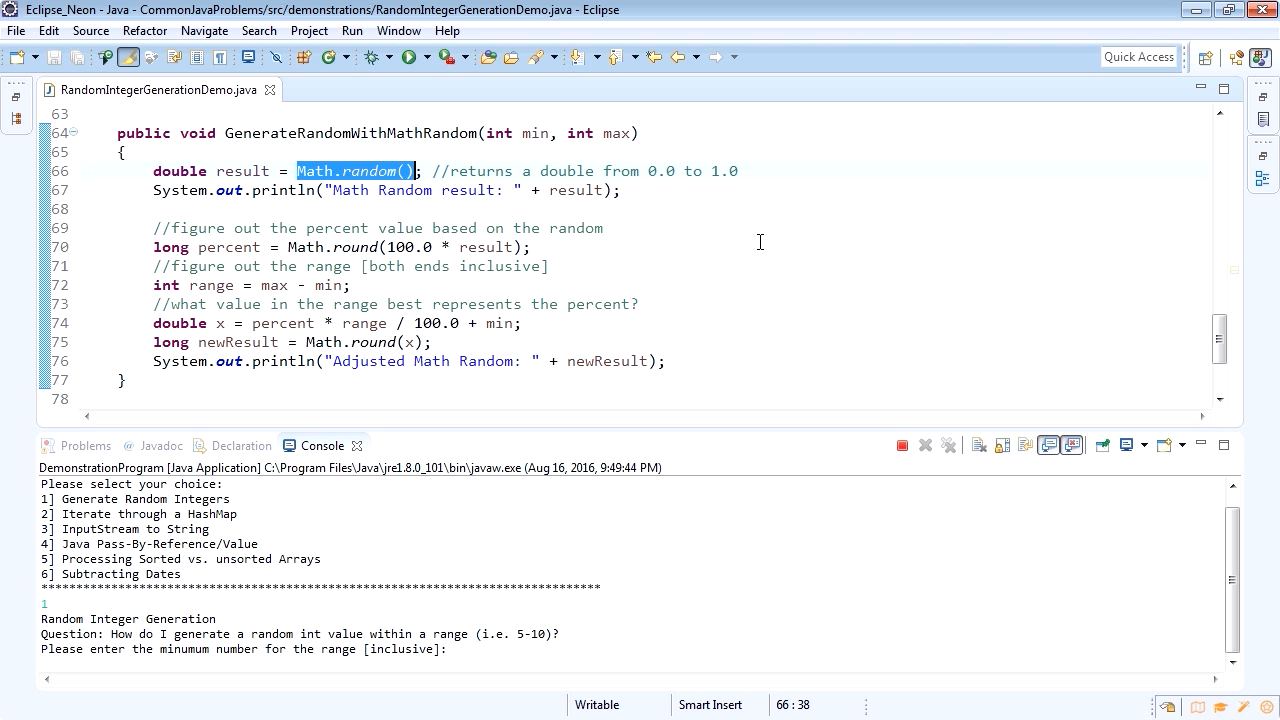 upper bound is non exclusive, you need to be careful if you want to add upper range in the random number generation (add 1 to the upper range to include it). If you don’t provide lower-bound, it will take lower bound as 0. Keep in mind the following important point while using the ThreadLocalRandom. (random_int_range) // 18 while we were running the code. Int random_int_range = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(lowerBound, upperBound + 1) * Generate random number with a given range of lower and upper bound. (random_int_with_upper_bound) // 6 while we were running the code. Int random_int_with_upper_bound = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(upperBound) * The upper bound is non exclusive i'e it will not be counted while generating the *generate random int within given range between 0 upper given bound. (random_int) //output will be different on different machine (2063277431 while running example) Int random_int = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt() //returns pseudorandom value Generate random number within given range. There can be 2 variations while generating a random numbers in Java or any other language. If you are using Java 1.7 or later, ThreadLocalRandom should be your standard way to generate the random numbers in Java. Generate Random Number Using ThreadLocalRandom Let’s see what are the different options and how to generate random numbers in Java. Java supports random number generation through ThreadLocalRandom, and classes. Normally, we came up with 2 types of requirements to generate a random number or generate a random number within a range. In this article, we will look at how to generate random numbers in Java. Generating random numbers in Java is a common requirement while working on Java application.
upper bound is non exclusive, you need to be careful if you want to add upper range in the random number generation (add 1 to the upper range to include it). If you don’t provide lower-bound, it will take lower bound as 0. Keep in mind the following important point while using the ThreadLocalRandom. (random_int_range) // 18 while we were running the code. Int random_int_range = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(lowerBound, upperBound + 1) * Generate random number with a given range of lower and upper bound. (random_int_with_upper_bound) // 6 while we were running the code. Int random_int_with_upper_bound = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(upperBound) * The upper bound is non exclusive i'e it will not be counted while generating the *generate random int within given range between 0 upper given bound. (random_int) //output will be different on different machine (2063277431 while running example) Int random_int = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt() //returns pseudorandom value Generate random number within given range. There can be 2 variations while generating a random numbers in Java or any other language. If you are using Java 1.7 or later, ThreadLocalRandom should be your standard way to generate the random numbers in Java. Generate Random Number Using ThreadLocalRandom Let’s see what are the different options and how to generate random numbers in Java. Java supports random number generation through ThreadLocalRandom, and classes. Normally, we came up with 2 types of requirements to generate a random number or generate a random number within a range. In this article, we will look at how to generate random numbers in Java. Generating random numbers in Java is a common requirement while working on Java application.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
